Medicinal Cannabis 101
Creating Nutritional Balance
Optimal physical and mental well-being can only be achieved by establishing and maintaining a balance of essential medicinal nutrients.
The History
Medicinal Cannabis has a long history.
It was first used as long ago as 400 AD and introduced into Western Medicine around 1840. In fact, it was used quite extensively up until prohibition in 1937.
The Medicine
Medicinal cannabis is derived directly from the cannabis plant. It is usually presented as either a whole plant extract, or a purified extract. Both presentations have certain benefits that might appeal to different users and applications.
Whole Plant Extract
Whole-plant extracts contain a specified amount of the cannabis plant’s most prominent cannabinoid(s) as well as all the naturally occurring active ingredients (terpenes/ flavonoids), working in harmony.
Purified Extracts
Purified Extracts are derived from the whole plant, undergoing a purification to isolate the desired cannabinoid(s) and removing most or all of the other active plant ingredients.

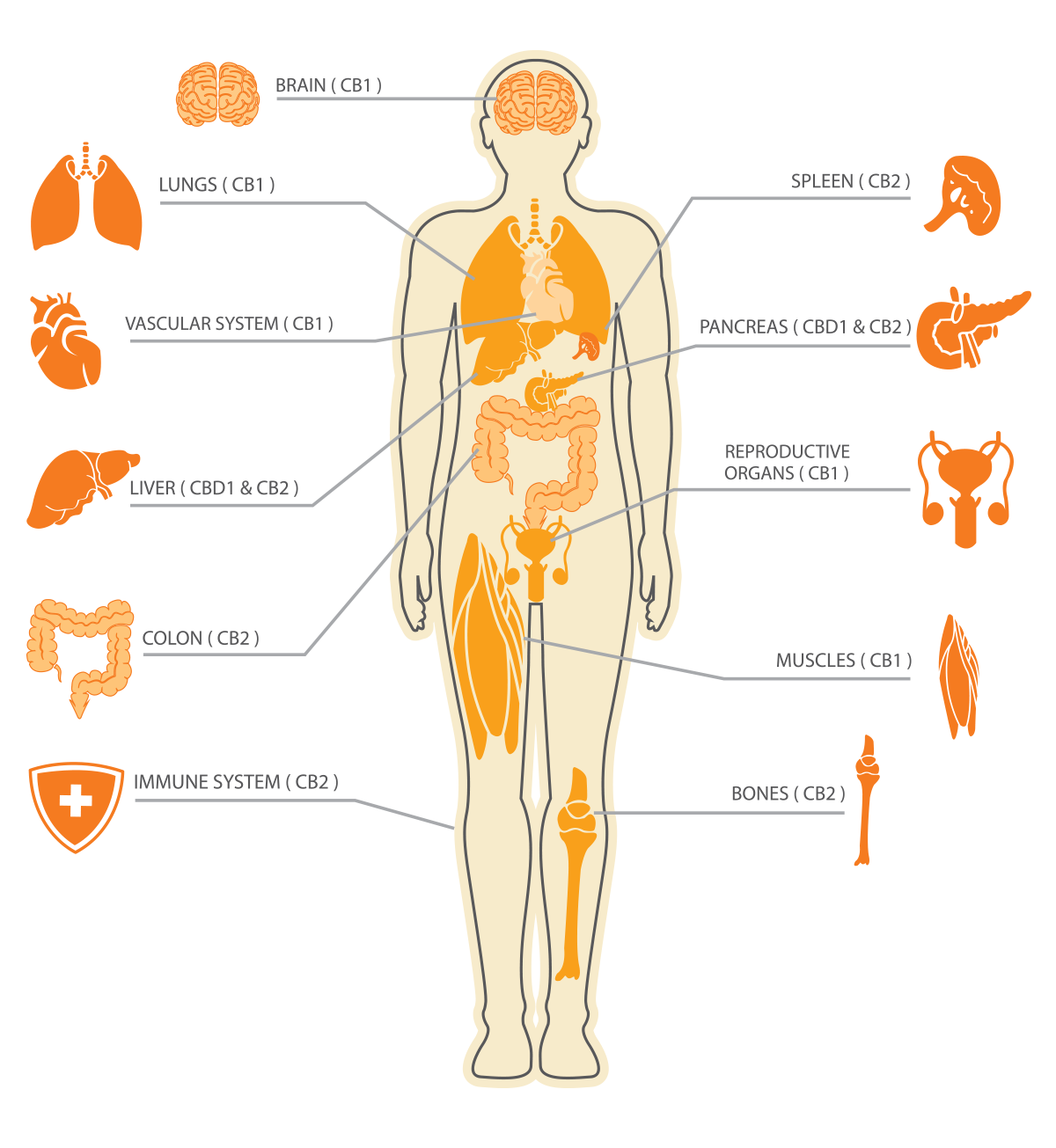
The Endogenous Cannabinoid System
The endogenous (originating in the body) cannabinoid system, often abbreviated to endocannabinoid system, or ECS.
1992 - ECS Discovered
In 1992, scientists discovered a system that was involved in a number of physiological processes.
Components of the ECS
- Endocannabinoids (Anandamide or N-arachidonoylethanolamine and 2-AG or 2-arachidonoylglycerol)
- Cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2)
- Enzymes - responsible for the breakdown of endocannabinoids
Role of the ECS
The role of the ECS is the modulation of a variety of organ systems to maintain the body’s physical and mental balance (homeostasis).
Under normal, healthy circumstances, our bodies ‘manufacture’ the two endocannabinoids mentioned above, but in some situations, including serious illness, it is believed that the balance is compromised.
Receptors
CB1 receptors are the most abundant of the two receptor types, and they are predominantly found in the central nervous system, in regions responsible for cognitive functions (eg hippocampus, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, basal ganglia, hypothalamus, amygdala).
CB2 receptors are prevalent in the immune and peripheral nervous system and tend to be responsible for physical wellbeing, such as immunity, inflammation and pain.
Cannabinoids and Characteristics
There are over 110 different cannabinoids that have been identified in the cannabis plant. The most commonly studied for medical use are:
Delta 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
Potential intoxicating effect
Pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties
May reduce nausea and vomiting and stimulate appetite
May have sedative properties
Cannabidiol (CBD)
Non-intoxicating
Pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties
May reduce anxiety
Anti-convulsant properties
Modulates effects of THC
Plant derived CBD and THC are both chemically similar to our body’s naturally occurring endocannabinoids, allowing them to interact with our cannabinoid receptors.
Treatment with Medicinal Cannabis
Medical cannabis is not currently available as a first line treatment. It can only be prescribed after conventional therapy has failed or is found to be not suitable (eg adverse effects) or ineffective.
To learn more about patient access and the regulatory framework please click below:
Types of treatment
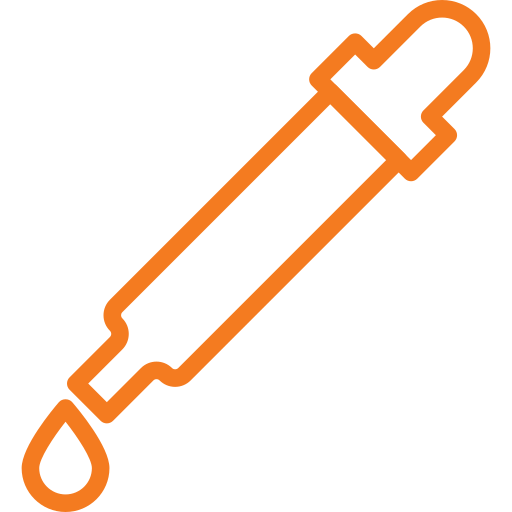
Oral
Mostly sublingual (drops under the tongue)
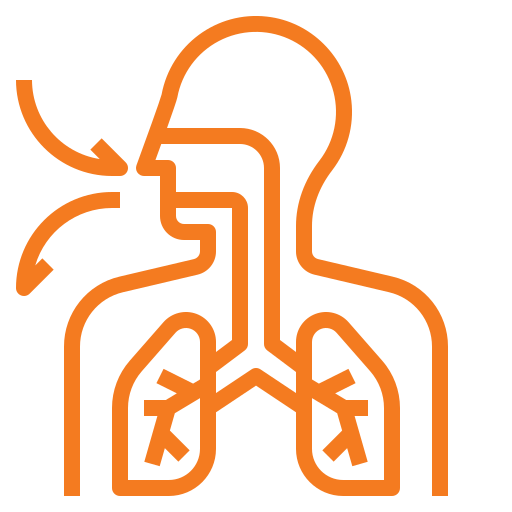
Inhalation/Vaporisation
Involving heating the cannabis

Transdermal
Across skin, topically applied eg cream or patches
Areas of Treatment
The TGA has provided guidance documents on a range of conditions and has published a non-exhaustive list of conditions that have been approved for the use of medicinal cannabis.
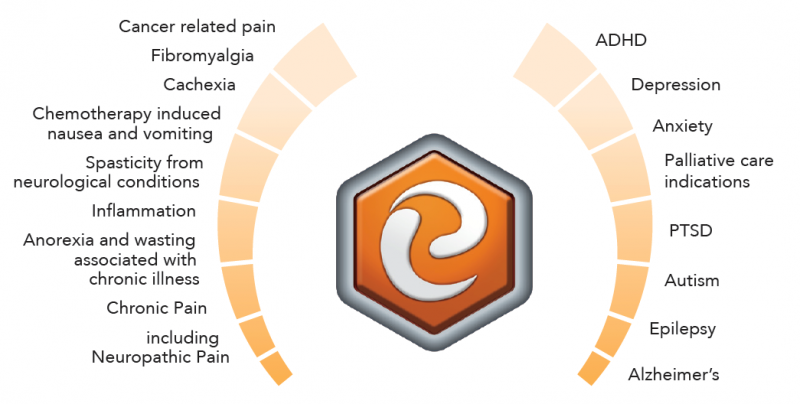
To learn more please register to our Education and Support Portal:
The Entourage Effect
In 1998, Professors Raphael Mechoulam and Shimon Ben-Shabat posited that the endocannabinoid system demonstrated an “entourage effect” in which a variety of “inactive” metabolites (terpenes and flavonoids) and closely related molecules markedly increased the activity of the primary endogenous cannabinoids, anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. They also postulated that this helped to explain how botanical drugs were often more efficacious than their isolated components.
Terpenes
Terpenes are fragrant essential oils that give various plants their characteristic aroma. They serve a protective function for the plant and have various therapeutic actions.
Terpenes have been shown to have analgesic or anti-inflammatory effects, amongst many other things.
To view and shop Entoura's range of Food Grade terpene products, please click here:
Flavonoids
Terpenes and flavonoids help enhance those therapeutic effects, as well as providing individual health benefits. Flavonoids have been shown to benefit the immune system.

